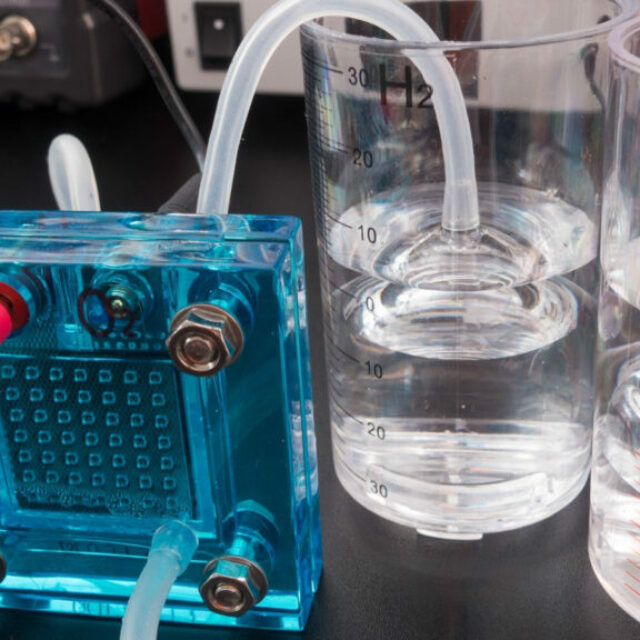
Flow Control Systems For Proton-Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. (PEMS)
Proton-exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) are a type of fuel cell that uses hydrogen and oxygen to produce electricity. PEMFCs are typically used in automotive applications, as they are efficient and have a small footprint. Mass air flow controllers, proportional valves, and pressure compensating valves play an important role in the function of PEMFCs. mass air flow controllers regulate the amount of air that flows into the fuel cell stack. This is important, as too much or too little air can negatively affect the performance of the fuel cell. Proportional valves are used to control the flow of reactant gas (hydrogen or oxygen) to the fuel cell. The valves are typically located at the inlet of the fuel cell stack.
Pressure compensating valves are used to maintain a constant pressure difference across the fuel cell membrane. This is important, as it helps to prevent reactant gases from leaking through the membrane. Together, these three valve types help to optimize the performance of PEMFCs by controlling the flow of reactants and maintaining a constant pressure difference across the fuel cell membrane.
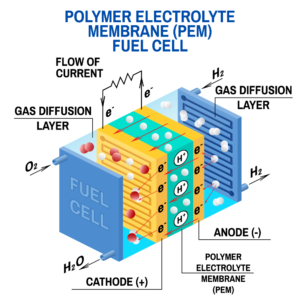
What is a (PEMFC)?
A Proton-Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC) is a type of fuel cell that uses an electrolyte membrane to separate the anode and cathode compartments. PEMFCs are often used in portable electronic devices, such as laptops and cell phones, because they are relatively small and lightweight.
One of the most important components of a PEMFC is the air control system, which regulates the flow of oxygen to the fuel cells. The oxygen flow sensor is used to measure the oxygen concentration in the fuel cells, and the mass air flow controller regulates the flow of oxygen to the fuel cells based on this measurement.
The PEMFC air control system is important because it helps to prevent the fuel cells from becoming overloaded and damaged. When the oxygen concentration in the fuel cells is too high, the fuel cells can become overloaded and may be damaged. PEMFCs are designed to operate at a specific oxygen concentration, and the air control system helps to ensure that the oxygen concentration remains at this level.
How do PEMFC’s stay cool?
PEMFCs are also equipped with a water control system, which regulates the flow of water to the fuel cells. The water control system is important because it helps to keep the fuel cells cool and prevents them from overheating.
PEMFCs are a promising technology for powering a variety of portable electronic devices. However, they have several limitations that need to be addressed before they can be widely used. One of the biggest challenges facing PEMFCs is the need for an efficient and reliable air control system. The air system is critical to the operation of PEMFCs, and it must be able to the flow of oxygen to the fuel cells with a high degree of accuracy.
Another challenge facing PEMFCs is the need for an improved water control system. The water control system is responsible for keeping the fuel cells cool, and it must be able to prevent the fuel cells from overheating. PEMFCs are a promising technology, but they face several challenges that need to be addressed before they can be used.
What kind of application utilize PEMFC
PEMFCs are a promising technology for powering a variety of portable electronic devices, but they have several limitations that need to be addressed before they can be widely used. PEMFCs are a promising technology for powering a variety of portable electronic devices. PEM fuel cells have several advantages over other types of fuel cells, including their high power density and their ability to operate at low temperatures. PEMFCs are also relatively small and lightweight, making them well suited for use in portable electronic devices.
One of the challenges that needs to be addressed in order for PEMFCs to be more widely used is the issue of flow control. PEMFCs require a constant supply of reactant gases (usually hydrogen and oxygen) in order to operate. The amount of reactant gas that needs to be supplied to a PEMFC can vary depending on the power output required from the fuel cell. In order to ensure that the correct amount of reactant gas is supplied to the PEMFC, a flow control system is needed.
The most common type of flow control system used for PEMFCs is a mass air flow controller (MAFC). MAFCs are devices that measure the mass flow rate of a gas and then control the flow of the gas by regulating a valve. MAFCs are used in a variety of different applications, including PEMFCs.
MAFCs can be used to control the flow of either hydrogen or oxygen to a PEMFC. In order to ensure that the PEMFC operates at its optimal efficiency, it is important to control the ratio of the two reactant gases that are being supplied to the fuel cell. This can be accomplished by using a proportional valve in conjunction with the MAFC. Proportional valves are commonly used in PEMFCs to control the flow of reactant gases.



